Many people do not realize that general aches and pains in the feet and body may be associated with hypermobility. Although hypermobility is common in Singapore, it is relatively unknown and is often found in association with flat feet.
There are two types of hypermobility syndrome:
- The first type is a localized condition that affects specific joints. Joint hypermobility is a condition featuring joints that easily move excessively over the normal range of motion common to the individual’s age, gender and ethnicity.
- The second type is more of a generalized hypermobility affecting bones and soft tissue. This may be accompanied by musculoskeletal symptoms, such as arthritis, muscle pain, or internal disruption to the joints (internal derangement). More severe forms of this hypermobility syndrome are associated with underlying conditions, like Marfan Syndrome, Ehrler-Danos Syndrome, and Muscular Dystrophy.
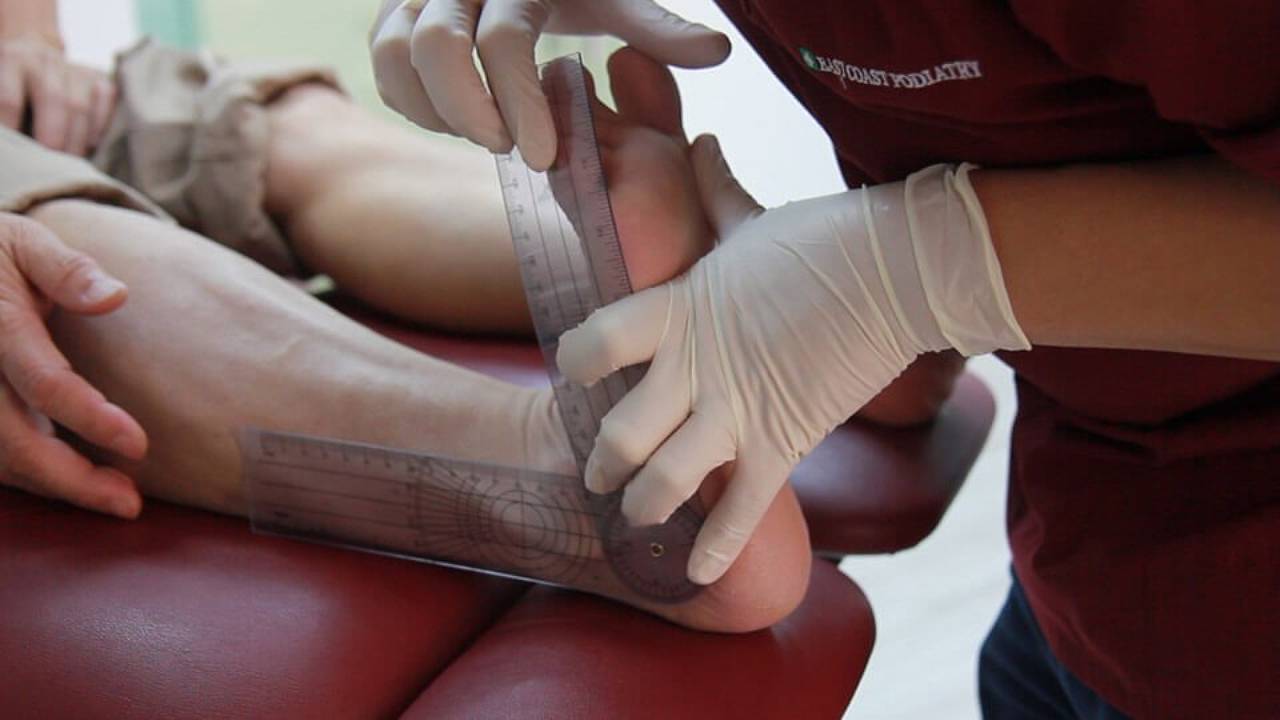
Hypermobility is more common among women than men and also tends to run in families. Asians are also more prone to have hypermobility due to a defect in the Tenascin-X gene, which is also responsible for the higher incidence of hypermobility in Singapore.
A significant portion of painful adult flat foot is due to joint hypermobility, as the arch of the foot collapses upon weight bearing. Other symptoms include, but are not limited to:
- pain in the joints
- weak or ineffective muscles
- clumsiness or lack of coordination
- problems with gait
- difficulty in writing
- clicking joints
- back pain
- frequent ankle sprains and injuries
- tripping and falling easily, particularly for kids
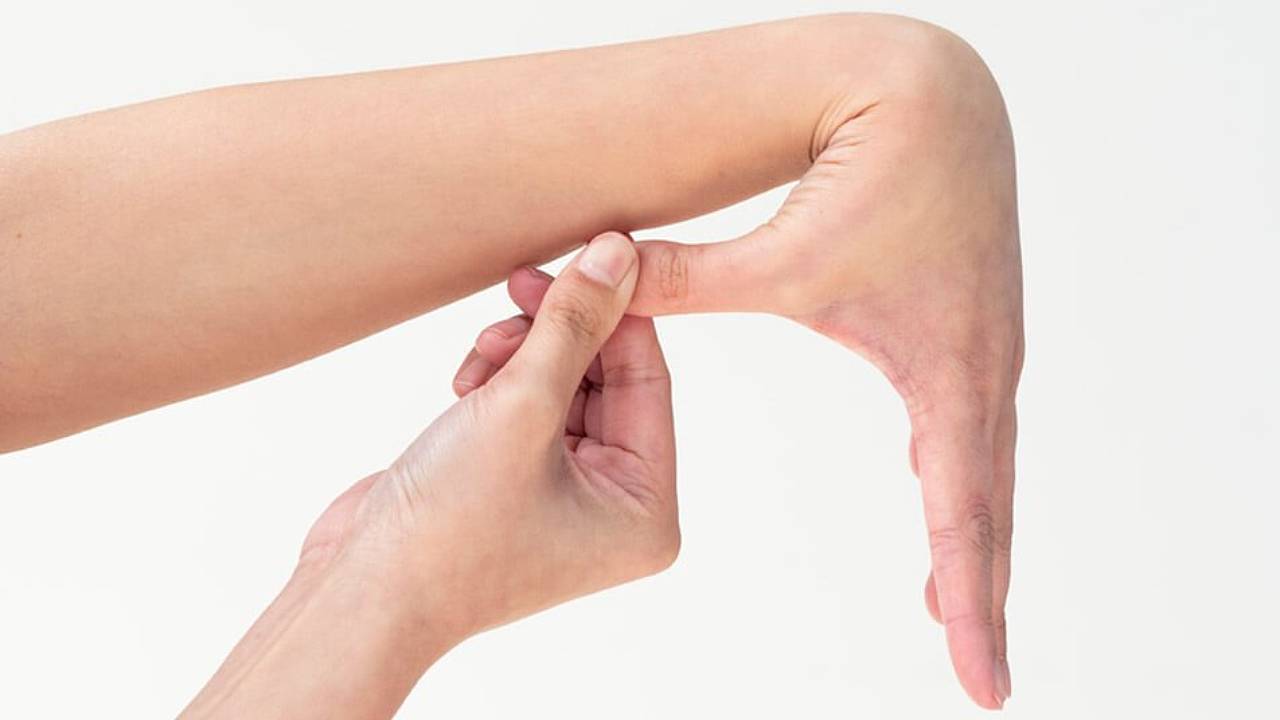
If you suspect you have hypermobility, there is a simple test known as the Beighton scoring system that you can perform at home.
- With your knees straight, bend at the waist and put your palms flat on the floor
- Each of your elbow that you can bend beyond 180 degrees
- Each knee that you can bend beyond 180 degrees
- Each thumb you can touch to your forearm when bent backwards
- Each little finger that you bend backwards more than 90 degrees
For each of the above that you are able to perform, add one point, the total will be your Beighton score. The maximum number of points is 9. For young adults, a result of 6 or more indicates joint laxity, otherwise known as hypermobility.
Not everyone with hypermobility requires therapy. If you do not experience any symptoms or hindrance to your lifestyle, there is no need for intervention. Some people with hypermobility are able to use their condition to their advantage in careers or hobbies such as gymnastics, ballet and dance. However, it is important to be careful not to overextend your joints, as this can lead to injuries.
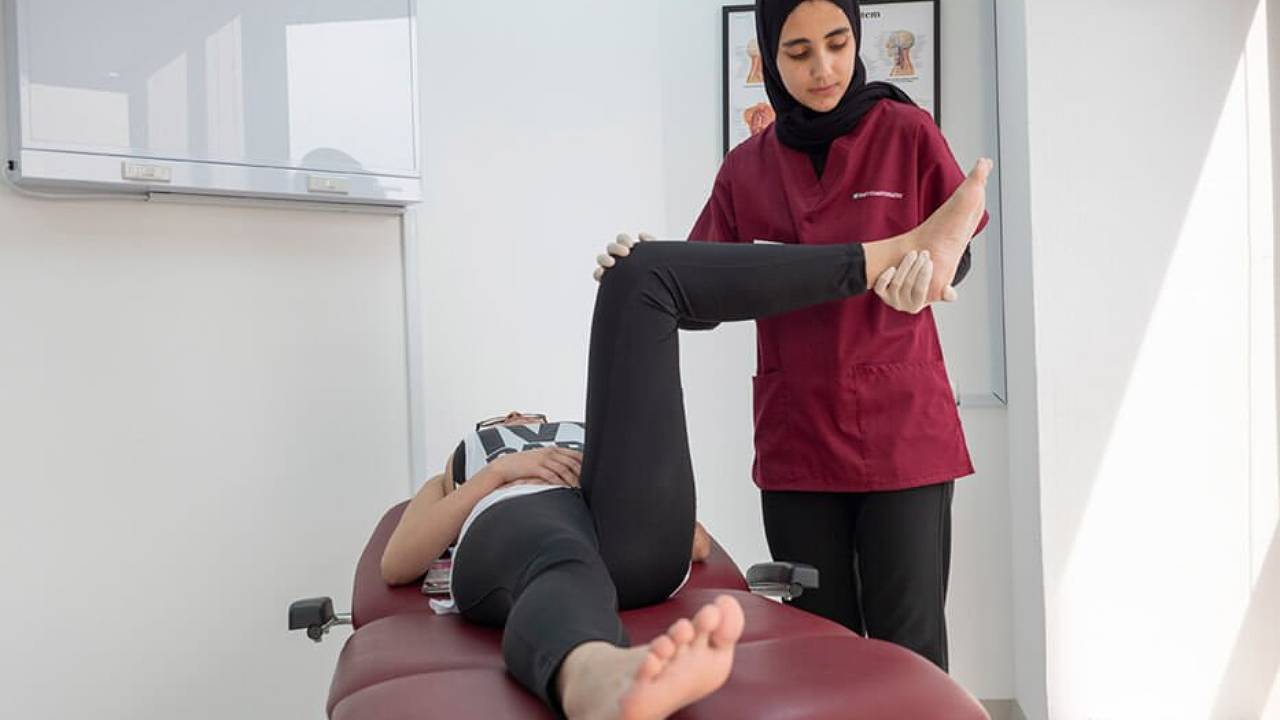
For some people, hypermobility can cause pain or discomfort. If left unresolved, it can lead to the development of certain conditions that can affect quality of life. Some of the consequences of hypermobility include:
- Scoliosis
- Malalignment syndrome
- Osteoarthritis
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction
- Recurrent sprains and dislocations
- Chronic pain syndrome
While some people with hypermobility may try stretching exercises to relieve muscle tension or pain, this is not advisable as it can further increase flexibility and laxity. The tension occurs because the muscles surrounding the joint tighten to compensate for the hypermobility. Once the hypermobility is addressed, the discomfort should improve.
To avoid overstretching, patients will be advised an appropriate exercise and stretching plan. Regular exercise and conditioning of muscles helps to protect and support the joints. Joints not supported by strong muscles run a higher risk of developing osteoarthritis.
Podiatrists can also help hypermobile persons improve joint stability. Using an orthotic device, such as a ankle foot orthotics or by wearing knee braces, podiatrists can correct the way the rest of the body moves to reduce incidences of ankle sprains and lower limb pain. On top of assisting to realign the feet, knees and hips, customised orthotic and such devices will also provide support for flat feet caused or exacerbated by hypermobility, and can also lower the likelihood of tendinopathies and arthritis.
If non-surgical options are not relieving your pain, surgical options to stabilize the joints from within can be explored.




