What is Plantar Fasciitis (Heel Pain)?
Plantar Fasciitis is a common painful condition caused by overuse of the plantar fascia. The plantar fascia is a broad, thick band of tissue that runs from under the heel to the front of the foot and helps support the arches of our feet. It is particularly susceptible to repetitive stress injuries induced by physical activities, including sports or work-related situations where a similar action is performed repeatedly, resulting in heel overuse.
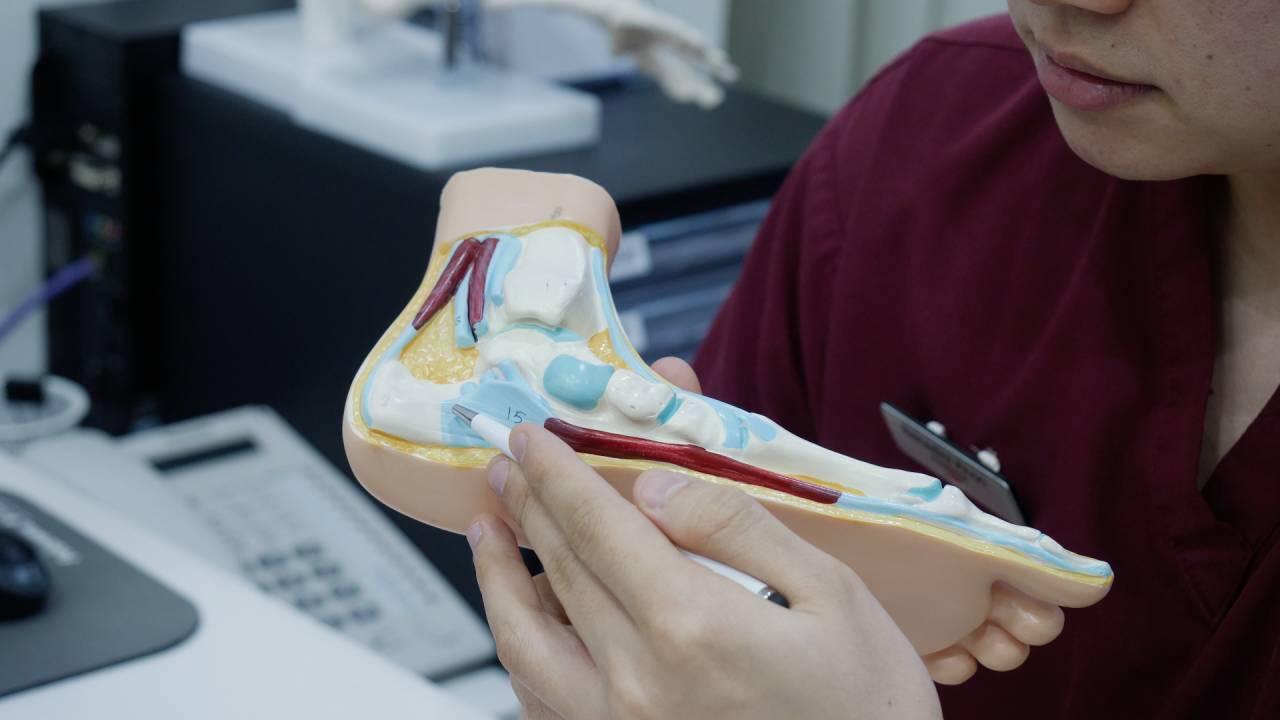

Signs and Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis Include:
- Pain in the underside of the heel
- Sharp pain in the morning when getting out of bed or when standing up after a prolonged period of sitting
- Pain when applying pressure around the heel
- Presence of swelling below the heel and around the ankle.
- Chronic pain may result in burning and tingling sensations extending from the heel region
Risk Factors
Some of the factors that lead to a greater chance of developing plantar fasciitis are:
- Being overweight or gaining a large amount of weight recently
- Having a job that requires prolonged standing
- Having a foot type that predisposes you to this condition
- Discrepancy in leg length
- Sudden increase in the level of physical activity
- Long-distance running
- Sports that incorporate much side-to-side movement such as tennis or basketball
What Happens if Plantar Fasciitis is Unresolved?
Plantar fasciitis refers to the initial inflammation of the plantar fascia as a secondary reaction to tissue microdamage. If this condition is ignored for more than 6-8 weeks, it develops into a chronic condition known as plantar fasciopathy.
At this point, anti-inflammatory drugs will no longer be effective, and symptoms will return unless different techniques are used. A specific and focused approach is required to repair the damage, as the plantar fascia will continue to degenerate and rupture if left unresolved.
Why do patients develop plantar fasciopathy?
- Did not know that they had plantar fasciitis
- Assumed the pain would resolve spontaneously
- Failed to address plantar fasciitis in time
- Attempted to resolve it with ineffective methods
At this point, depending on the patient’s age, activity level, and goals, the condition may require stabilising devices or surgical intervention.
Types of Approaches
Home remedies such as R.I.C.E (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) can be performed in minor cases of plantar fasciitis:
- Rest by avoiding activities that put stress on the heel and arch of the foot
- Ice the affected area for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day to reduce inflammation and pain
- Compression can be performed using an elastic wrap or bandage to wrap affected foot, this helps reduce swelling
- Elevate the affected foot to help reduce swelling
If you continue to experience pain or if it seems to be worsening, it is important to consult a healthcare professional such as a podiatrist.
They will be able to diagnose the cause of your pain and recommend the best approach for your condition.
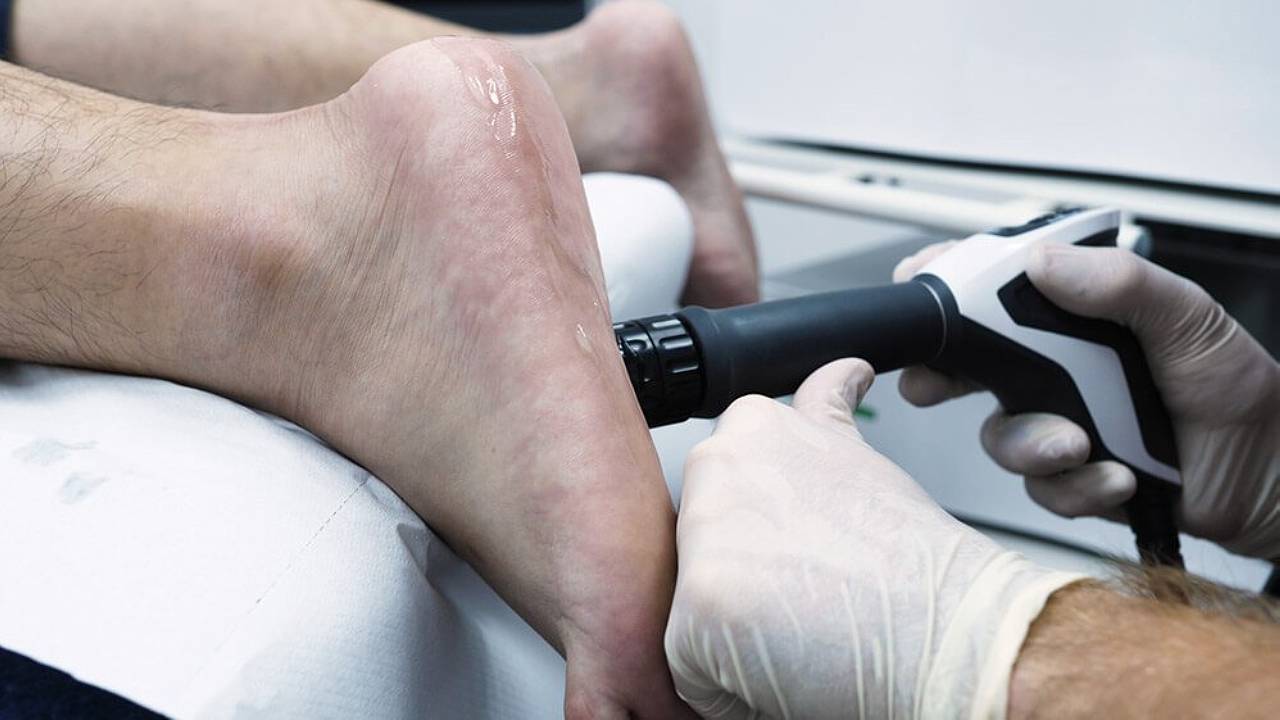
These non-invasive therapy include:
- Extracorporeal shockwave therapy
- Super Inductive Therapy
- Arch taping
- Physical therapy
- Custom orthotics
One common therapy for plantar fasciitis is to inject steroids into the affected area. Steroids can reduce inflammation and provide pain relief, but they do not address the underlying cause of the condition. As a result, the pain may return, and there is an increased risk of further damage, such as ligament rupture. In some cases, this can lead to more complex and pain during therapy in the future.
In the most severe cases of plantar fasciitis, surgery may be necessary. However, surgery is not without risks, and it can also affect the long-term strength and function of the foot arch. Therefore, it is important to diagnose and manage plantar fasciitis as early as possible with the appropriate technologies. Early diagnosis and therapy can help to prevent the condition from becoming severe and reduce risk of complications.




