What is plantar nerve neuritis
The term ‘neuritis’ refers to an inflammation of a single or group of peripheral nerves. Plantar nerve neuritis can be found in two forms; a standalone condition where the lateral branch of the inferior calcaneal nerve becomes inflamed and irritated over a period, or more commonly as a complication associated with chronic plantar fasciitis.
In some cases, those suffering from chronic or unresolved foot or heel pain may also have periods of pain-free episodes. However, this does not mean that the condition is resolving, as underlying nerve conditions can still be a cause for concern.
Causes
The most common cause of plantar nerve neuritis is the repetitive irritation or impingement of nerves due to compression around the soft tissues of the ankle area. These nerves can be easily damaged due to injury or trauma in other parts of the foot, for example, a microtear in the plantar fascia.
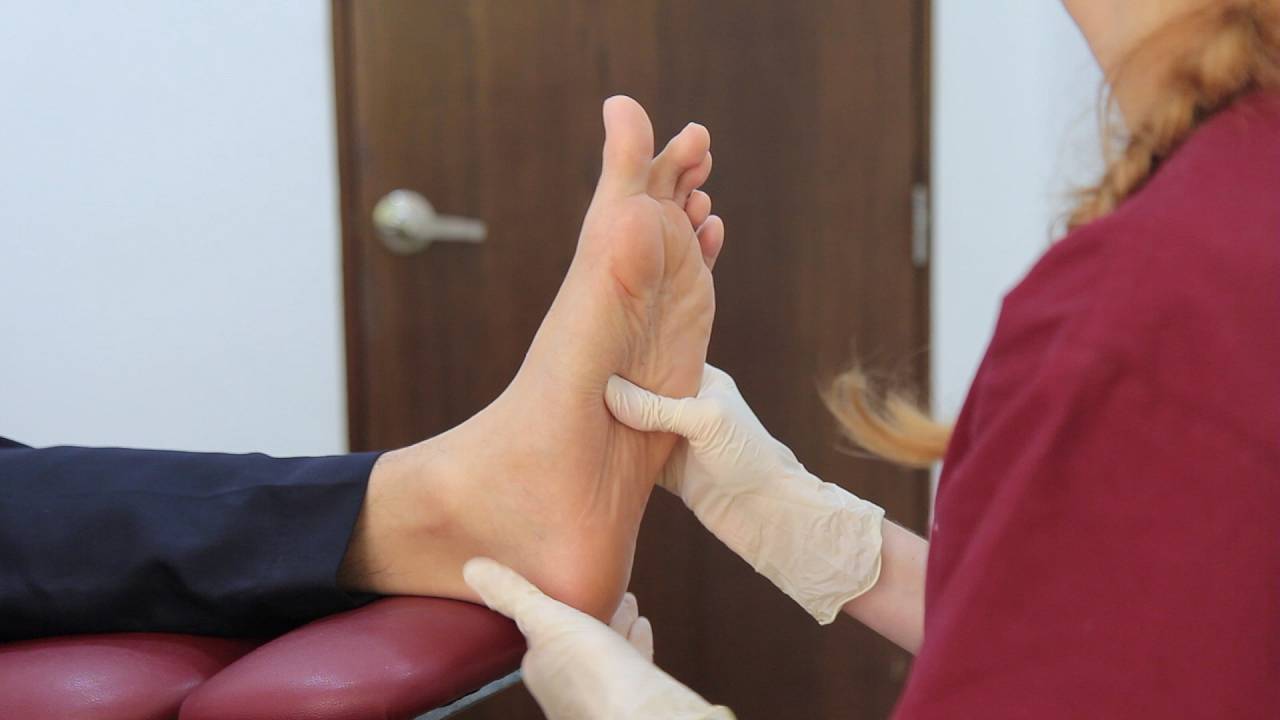
Sign and symptoms
The inflammation of the medial and lateral plantar nerves can result in pain and a loss of function to the linked intrinsic foot muscles, and can result in:
- Gradual increase in pain over time
- Constant pain that radiates to the lower part of the heel and ankle
- Worsened pain with forceful or continuous activity
- Difficulty when pressure is applied to the foot during walking, standing, or sitting
If left unresolved, this can lead to inflammation and symptoms such as numbness, tingling, burning, and cramping. In some cases, it can also cause long-term nerve damage, such as scarring or neuromas.
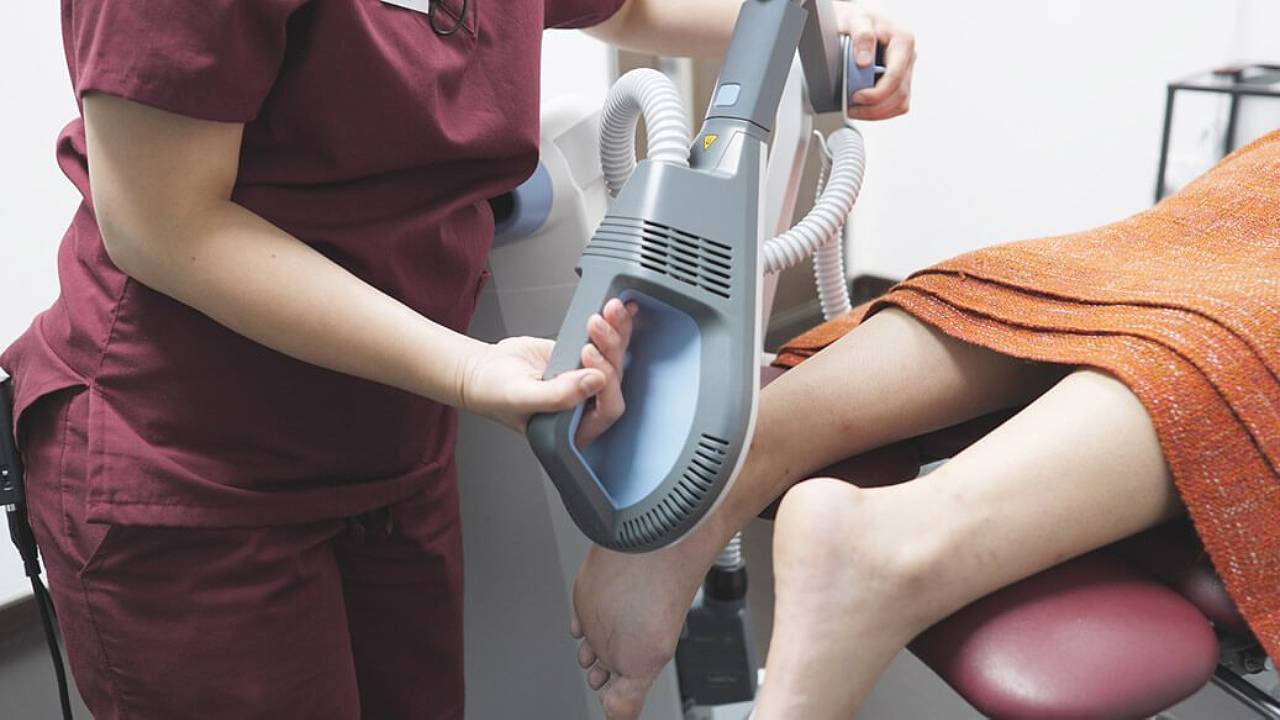
How do I manage?
A podiatrist will design a plan with two goals:
- To reduce pain and severity of symptoms
- To address the primary cause of the condition
Depending on your assessment, a combination of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy (SIS) and Extracorporeal Magnetotransduction Therapy (EMTT) can be utilised to reduce inflammation and provide pain relief. Long-term offloading in the form of custom orthotic devices may also be required to address the repetitive impact and reduce nerve impingement.
Individuals with heel pain are advised to consult a podiatrist promptly. If left unaddressed, it can aggravate and result in complications. Early diagnosis and a combination of different therapies that can help accelerate the recovery process, ensuring that the patient is back on their feet as soon as possible.




