What is the Plantar Plate?
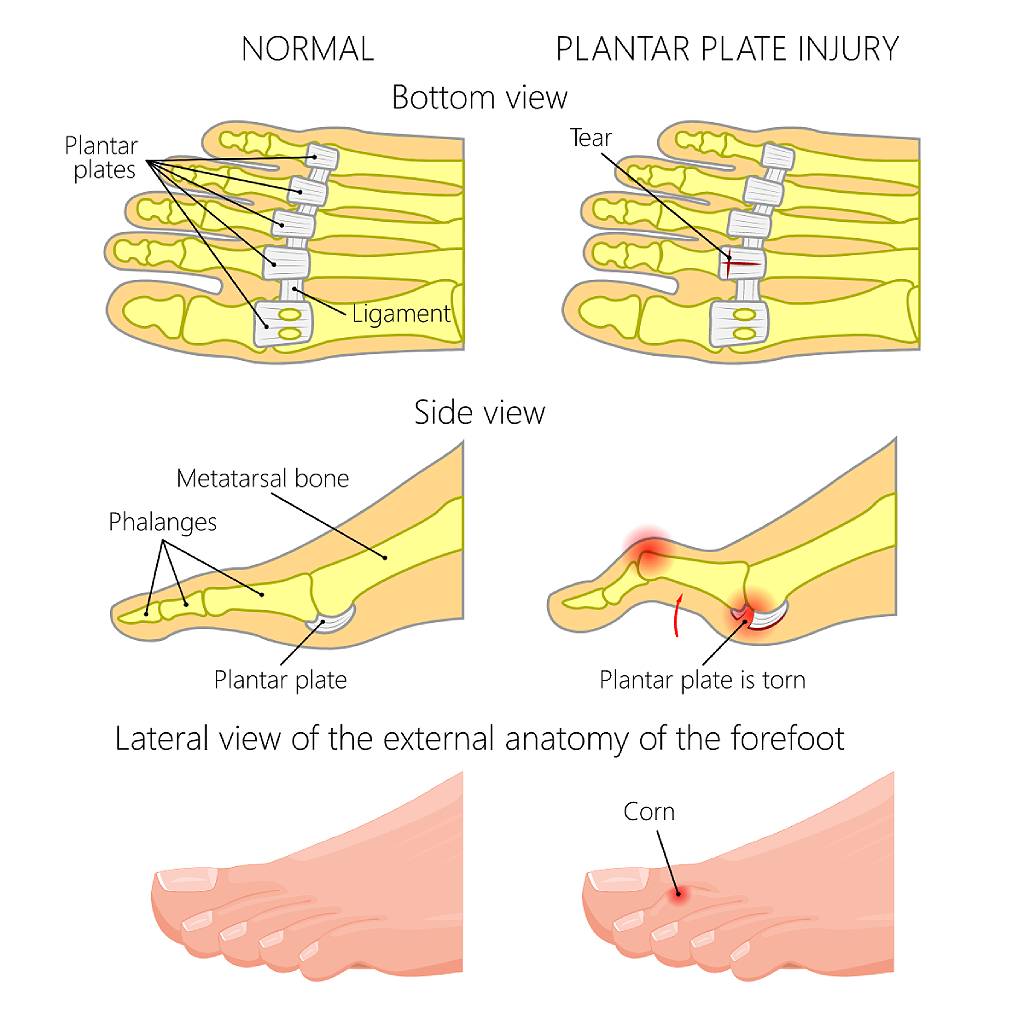
The plantar plate is a thin structure directly under each metatarsal joint of the foot that connects the metatarsal to the distal phalanx. These structures help support and stabilise the forefoot while protecting the toe joints when under stress or during movement.
The plantar plate is subjected to significant repetitive tension from ground reaction forces transferred through the forefoot during movement, resulting in acute injuries or stress trauma over time. Although injuries can occur to the plantar plates of each of the lesser toes, this condition most commonly affects the plantar plate of the second. Hammer toes, floating toes, dislocations, and toe separations are also typical associated conditions of plantar plate tears.
Symptoms of Plantar Plate Ruptures
Plantar plate ruptures occur when stress upon the thin structure exceeds the threshold and causes a tear, causing symptoms such as:
- Sharp pain and/or swelling under the ball of the foot extending towards the toes
- Pain that is most commonly found at the base of the 2nd and 3rd toes and intensifies when barefoot or tip-toeing
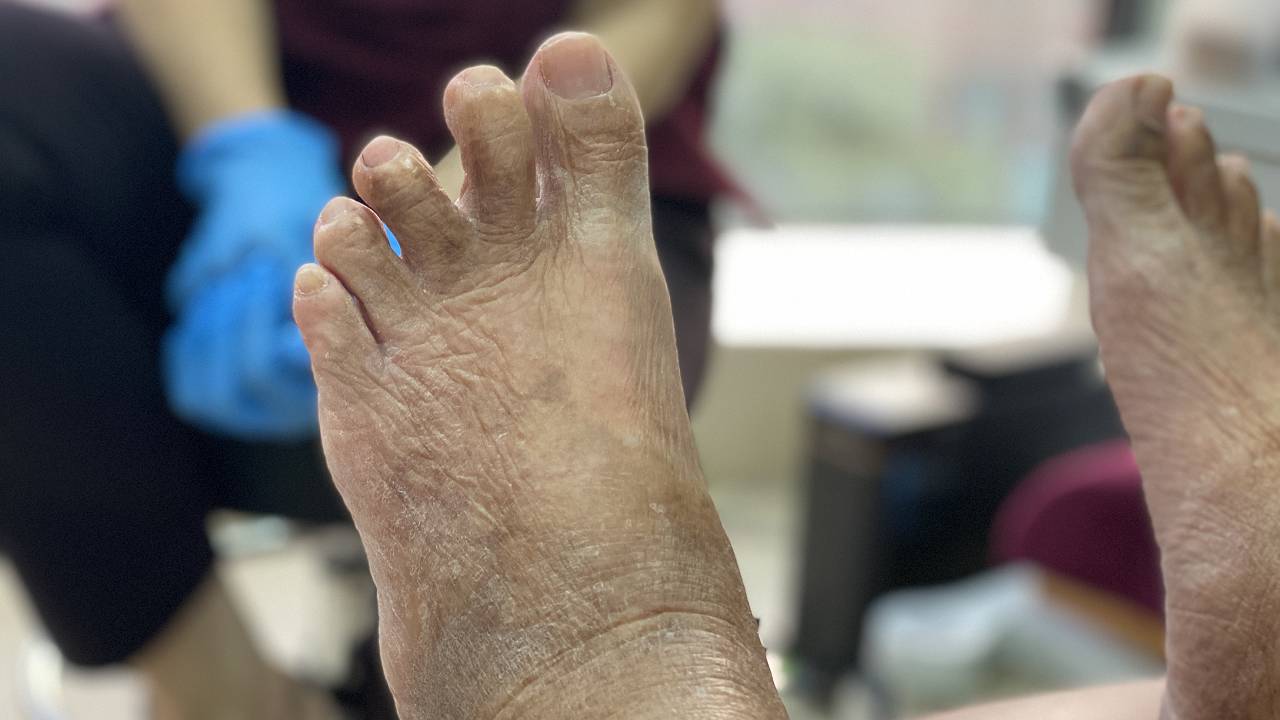
In more severe cases, a visible deformity in the toes may develop, giving the appearance of splayed apart toes, known as a ‘Daylight Sign’. This is a clinical indication of a plantar plate rupture.
Causes
Although the thin plantar plate is very strong, overuse can cause the structure to weaken and eventually rupture. Individuals are at increased risk of rupturing the plantar plate if they:
- Transfer excessive forces through the forefoot
- Overpronate
- Have hypermobile feet
- Have high arches
- Have a long 2nd toe (Morton’s toe)
This condition is common and affects individuals of all age groups and genders. It can often be seen in individuals who have made sudden increases in physical activity; changes such as beginning a fitness program or training for a marathon can cause symptoms to present and increases the risks of a partial or complete rupture.
Types of Approaches
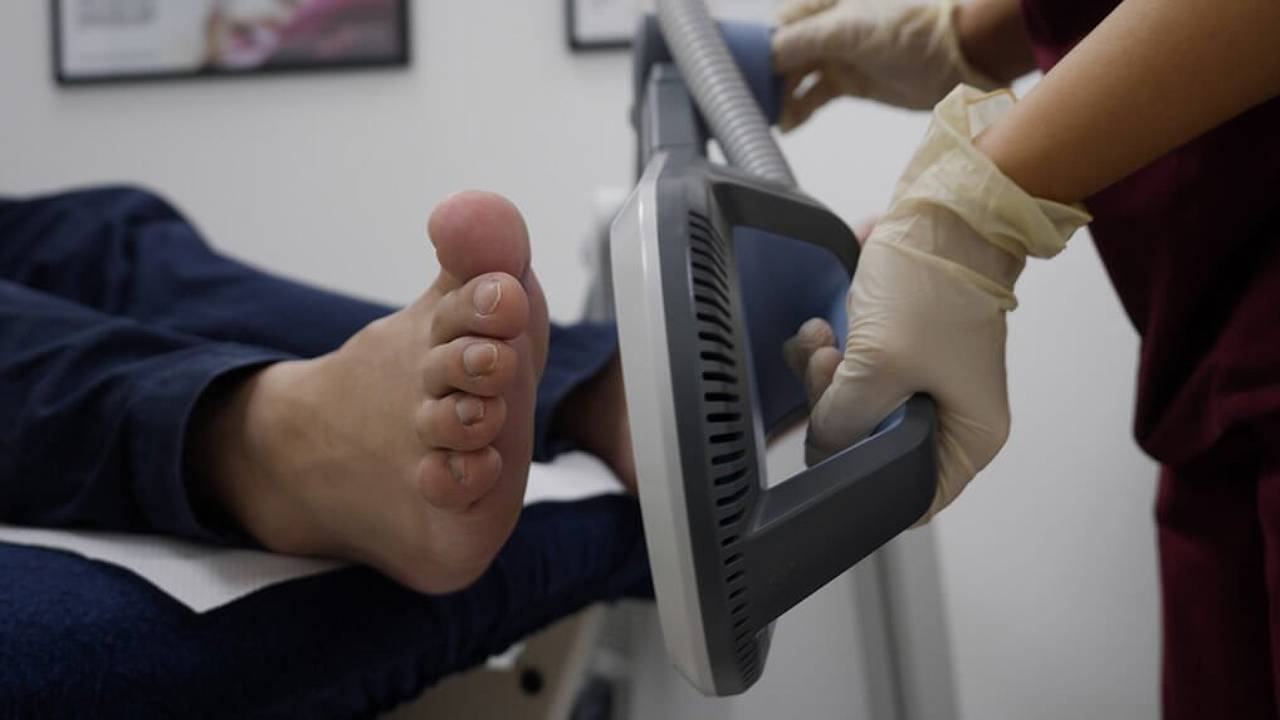
Early diagnosis is critical for most conditions, as it can improve your chances of a full recovery. Before a podiatrist can help, a comprehensive history and diagnostic assessment are required. Ultrasound imaging can be used to determine the extent of the tear and identify any underlying or secondary conditions.
The first goal is to reduce symptoms. The second goal is to stimulate healing and begin rehabilitation of the affected structures.
Depending on the patient’s assessment, options may include extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) and Super inductive System therapy, and custom foot orthotics. This will help reduce pain, stimulate recovery, and prevent further injuries.
If a plantar plate injury is left unresolved, it can lead to the dislocation and development of osteoarthritis or osteonecrosis of the affected joint. This is because the abnormal pressure on the joint can cause the cartilage to break down and the bone to die. Therefore, it is important to seek help from a medical professional to prevent it from aggravating.
While the best solution will vary depending on the individual’s condition and how they respond to it, a multi-pronged approach that focuses on symptom reduction and rehabilitation often produces the best results.




